
How To Speed Up WordPressⓇ Sites
In today’s fast-paced digital world, website speed is critical. Slow-loading pages are a major cause of WordPressⓇ[1] site abandonment, impacting everything from user experience to customer retention.
If your website loads slower than it should, there’s little doubt that it’s directly affecting your traffic and your bottom line. After recognizing this fact, many developers and business owners are left wondering how to speed up WordPress sites. This guide will help you understand the importance of fast loading times and provide tips for increasing your WordPress site speed.
Key takeaways:
- Reducing load times by one second increases conversion rates by 17%. Conversely, a 100-millisecond delay causes a 7% drop. Speed is a primary driver of revenue and retention.
- Bounce rates jump from 9% to 38% when load times increase from two to five seconds. Maintaining sub-two-second speeds is critical for sustaining user engagement.
- Mobile visitors abandon 53% of sessions if pages take over three seconds to load. Prioritizing mobile performance is essential for audience retention and growth.
- Integrated caching and global Content Delivery Networks minimize latency for international audiences. These tools provide the stability required to handle significant traffic surges.
- Establish a baseline by testing site speed monthly and auditing third-party plugins. Evaluate whether your hosting platform provides native performance features.
Why speed up WordPress sites?
WordPress is a powerful CMS that has taken the world by storm, powering over 800 million websites—that’s more than 40% of the entire internet!
However, the very themes, plugins, and tools that enhance your site’s functionality (and help make WordPress so popular) can also slow down performance, leading to higher bounce rates, lower user retention, and poor search engine rankings.
Optimizing these elements is crucial when it comes to speeding up your WordPress site. Proper management of themes, images, plugins, and other content ensures a seamless user experience and better SEO.
It’s important to note that every content management system must load all related items, whether visible on the page or running in the background, before delivering the full experience to site visitors. Fast-loading speeds are essential here because slow pages frustrate visitors, leading them to leave your site before fully engaging with your content.
With that in mind, making sure your site loads quickly can significantly enhance visitor satisfaction and keep them on your site longer.
What slows down your WordPress website?
Several factors can negatively impact your WordPress performance and loading times. Understanding these common culprits is the first step to implementing effective WordPress speed optimization. Some of the most common causes of slow WordPress site speed include:
- Heavy or poorly coded plugins: Plugins are a helpful way to optimize your site, but they can also add significant server processing time and database queries, slowing down response times and potentially impacting interaction metrics like First Input Delay (FID) or Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
- Unoptimized images: Large image file sizes are a major contributor to slow loading, directly affecting Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) as browsers struggle to download and render them.
- Excessive HTTP requests: Loading too many separate CSS files, JavaScript files, or external resources, can delay First Contentful Paint (FCP) and LCP.
- Bloated themes: WordPress themes packed with unused features can contribute to slower load times due to excessive code.
- Inadequate or slow web hosting: It’s important to have the right hosting provider for your site. Slow web hosting results in high Time to First Byte (TTFB), acting as a bottleneck before the page even starts rendering.
- Site caching: A lack of effective caching (both server-side page caching and browser caching) means WordPress has to rebuild pages dynamically for each visitor, increasing server load and TTFB.
- Outdated versions of PHP: Using an outdated version of PHP can significantly hinder backend performance, as newer versions offer substantial speed improvements.
Identifying these issues often involves using speed testing tools which highlight specific bottlenecks tied to metrics like Core Web Vitals, guiding your efforts to improve WordPress website speed.
The importance of accelerating your WordPress site speed
The nostalgic screeching of a dial-up modem signaling that your page will load eventually is now the stuff of technological history. These days, consumers expect web pages to load quickly every single time. In fact, 40% of this survey’s respondents said they would abandon a site if it takes longer than three seconds to load.
The best thing you can do for your business is have a fast WordPress site. Without it, you’ll almost certainly lose valuable traffic and even more valuable revenue. That’s because online consumers are slightly impatient—over half of all mobile users admit to abandoning a page based solely on its slow loading time. It’s also worth noting that for every second a site loads faster, the conversion rate of that site improves by 17%.
Even worse, if your websites have slower speeds, that fact may prevent potential consumers from ever even finding you. For Google, page speed has been a ranking factor for mobile searches since July 2018. This means a slow site will negatively affect your SEO ranking. If there was ever a time to learn how to speed up WordPress sites, now is that time.
Essential tips to drastically speed up WordPress sites for mobile users
While the ubiquity of mobile devices and mobile use isn’t exactly news, you might not know that speed plays a huge role in the way Google indexes mobile searches. If your site is a little slow but still strongly relates to certain search terms, you can achieve a decent ranking. However, Google does prioritize faster mobile sites.
About 15% of Americans identify as “mobile-only” internet users. So, selecting plugins grounded in responsive design principles can effectively speed up WordPress site performance, providing a smoother experience for the majority of your users.
How to check your WordPress website speed
Before you can improve WordPress website speed, you need to measure its current performance. Several excellent tools are available to analyze your site and provide actionable insights. Popular choices include Google PageSpeed Insights, WebPageTest, GTmetrix, and the specialized WP Engine Website Speed Test. Here’s a general process:
- Choose a Tool: Select one of the tools mentioned above. Google PageSpeed Insights is great for Core Web Vitals analysis, while WebPageTest offers very detailed waterfall charts.
- Enter Your URL: Input the full URL of the page you want to test (start with your homepage, but also test key landing pages or product pages).
- Run the Test: Initiate the analysis.
- Analyze Key Metrics: Pay attention to metrics like:
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): Measures server responsiveness. High TTFB indicates server-side or hosting issues.
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): Time until the first piece of content (text, image) is displayed.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Time until the largest visible element (often a hero image or text block) is fully loaded. A key Core Web Vital.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability; how much content unexpectedly shifts during loading. Another Core Web Vital.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) / First Input Delay (FID) / Total Blocking Time (TBT): Metrics related to how quickly the page responds to user interactions. INP is replacing FID as a Core Web Vital.
- Review Recommendations: Tools provide specific suggestions based on their findings, often linked directly to slowing factors like unoptimized images or render-blocking resources.
- Test from Multiple Locations/Devices: Use tool settings (especially in WebPageTest or GTmetrix) to test from different geographic locations and simulate various devices (desktop, mobile) and connection speeds. This gives a more realistic view of user experience for your diverse audience and is crucial for assessing overall WordPress speed.
Effective strategies to speed up WordPress site loading time
So, just how fast is fast enough? Google reports that the best practice is to keep your loading times at three seconds or less.
Pages that take five seconds or more to load have a drastically increased probability of a bounce. If you want to retain visitors rather than drive them away, you need to strive for average loading times of less than three seconds (and ideally quicker than that).
Optimal WordPress settings for performance
- Limit Post Revisions: By default, WordPress saves numerous revisions for each post and page update. This can quickly bloat your database. Limit revisions by adding `define( ‘WP_POST_REVISIONS’, 3 );` (replace ‘3’ with your desired number) to your `wp-config.php` file, aiding WordPress performance.
- Disable Pingbacks and Trackbacks: These create notifications when other sites link to yours, but they also generate database entries and can be a source of spam. Disable them under Settings > Discussion by unchecking “Allow link notifications from other blogs (pingbacks and trackbacks) on new posts.”
- Manage the Heartbeat API: The WordPress Heartbeat API allows for real-time communication between the browser and server (used for auto-saves, login status, etc.), but frequent checks can increase server load. Use a plugin like Heartbeat Control to limit its frequency or disable it on specific pages where it’s not needed.
- Set the Correct Timezone: Ensure your WordPress timezone (Settings > General) matches your actual location. This guarantees that scheduled posts publish correctly and other time-dependent tasks execute as expected, preventing potential issues.
- Display Post Excerpts: On archive pages (like your main blog page or category pages), showing full post content can significantly increase load times. Configure WordPress to show summaries/excerpts instead under Settings > Reading by selecting “For each post in a feed, include: Summary” or check your theme’s customization options. This simple change contributes positively to WordPress speed optimization.
- Review Media Settings: While WordPress automatically creates different image sizes upon upload (Settings > Media), ensure these sizes align with your theme’s requirements. Avoid uploading excessively large images initially, relying instead on optimized versions.
Effective methods to speed up WordPress site performance
If you want to do your part to increase your WordPress site speed, there are a variety of simple tactics you can try on your own. Allowing your site to be cached by your host is one of the simplest ways. Here are a few other tips you can use, but please note that we recommend testing any changes in a local development environment before updating anything on your live site.
1. Enable Page Speed Boost for your
WP Engine-hosted sites
Page Speed Boost is an all-in-one tool that allows you to optimize your code, significantly improve page load times, and supercharge your SEO in minutes, all without technical expertise.
Available on WP Engine’s managed hosting platform, Page Speed Boost increases PageSpeed scores by up to 60% and enhances Core Web Vitals metrics for a better user experience. Faster-loading pages boost SEO, leading to higher search engine rankings. Optimized site code and images ensure a smooth experience across desktop and mobile devices.
Featuring more than 30 automated enhancements, Page Speed Boost reduces plugin conflicts and improves overall site performance. And unlike other optimization plugins, it operates as a background service, ensuring it doesn’t slow down your WordPress application while handling the majority of optimizations listed below
With an easy, one-click activation in the WP Engine User Portal, Page Speed Boost simplifies effective site optimization for marketers and developers alike. Find out more here!
2. Conduct a site speed diagnosis to accelerate your WordPress performance
Understanding how fast your website loads is the next step towards improving site performance. Tracking site speed is advisable should you install a plugin or make some other change to your site and want to see how it affects site load times.
3. Delete unused plugins and themes
Aside from the fact that you should always keep your plugins and themes up to date, deleting unused ones is the next step to a speedy site. Not only do unused plugins and themes present security vulnerabilities, but they can also detract from WordPress website performance.
To delete the unused WordPress plugin, you’ll first need to deactivate it. Then you can go to your inactive plugins list and delete the ones you no longer want.
To remove an unwanted WordPress theme, simply go to Appearance > Themes to delete the ones no longer in use.
4. Clean up your media library
Another simple solution to resolve performance issues is to remove unused media. Over time you might start to accumulate images that are no longer used. To free up space, you should consider removing unused media.
If you want to remove unused media manually, you can use a plugin like Media Cleaner to dispose of unused media or you can do so manually. Then, in order to manually remove unused media, simply go to Add Media -> Media Library -> Unattached and then delete those files no longer in use.
Learn more about how to clean up your WordPress media library in this helpful article.
5. Clean up your database
If left unchecked, your WordPress database will start to accumulate clutter over time. This unnecessary bloat can slow down your site. However, with regular cleanups, you can reduce your database size for faster loading.
For instance, post revisions can take up a huge chunk of unneeded space. If you have a post which is 100KB of data and there are five revisions of that post, the total space wasted is about 500KB.
Cleaning up your database can be done manually through phpMyAdmin, although the process can be tricky and damaging if you don’t know what you’re doing. If you aren’t a technical whiz, installing a plugin to accomplish this task is the safer way to go. WP-Sweep and Advanced Database Cleaner are both safe bets for combing through your database and getting rid of things like old revisions, spam comments, MySQL queries, and more.
6. Remove render-blocking JavaScript and CSS
If you’ve been using page test tools to test your website’s speed, you may have run across this recommendation which can be difficult to understand. If you look at your page’s waterfall view using a tool like webpagetest.org or Pingdom, you’ll likely see that there’s a number of JavaScript files (.js files) loading before your “start render” line. This is known as “render-blocking JavaScript”.
The core function of JavaScript is to perform an action on a web page, like a popup or rotating images in your slider. In reality, these actions don’t need to be loaded until your site fully loads the content and styles. So by “Defer JavaScript Parsing,” these tools are really saying, “load this stuff later on in your page instead of at the top.”
7. Minify CSS, HTML, and JavaScript
Over time, CSS, HTML, and other source code files can build up and cause your site to run like molasses. To give your site a speed injection, you should consider minifying its code.
Through minification, the backend of your site will be optimized to be a lean machine. This technique works by reducing the file size of HTML, JavaScript, and CSS files and removes unnecessary characters, like spaces, line breaks, and comments. The result is a reduced amount of data transfer required so that files run quicker and your web pages load faster. While WP Engine’s Page Speed Boost minifies code as part of its wider feature set, there are also a number of plugins built for this specific task. WP Rocket, which helps with site optimization, including minification, is a popular choice, while CSS Compressor is another good option that simplifies CSS code.
8. Optimize images
Images are imperative to keeping a site visitor engaged. While your site may contain a ton of beautiful imagery, it’s a good idea to optimize these images to achieve faster page load times. There are multiple ways you can optimize your images, including compressing images, adding alt text and titles, and creating an image sitemap. To learn more about how you optimize images, check out this article, How To Optimize Your Images For WordPress.
9. Lazy-Load long pages
For one-page sites and sites which have a long home page, Lazy Loading can be a real time saver. Lazy Loading essentially prevents the elements lower down on your page from being loaded until the visitor scrolls down to see them. By not loading all of the content of your long page at once, your site can begin rendering faster. A common plugin used for lazy loading is Lazy Load by WP Rocket.
10. Modernize your stack with WP Engine Newsroom
For high-growth publishers, site speed is often hampered by a fragile patchwork of disconnected plugins. Newsroom utilizes native features like Live News and Editor Tabs to eliminate the heavy database queries and “collision” errors that typically spike latency during high-velocity reporting. This unified approach reduces tech debt and ensures your site remains stable for readers while protecting vital ad revenue.
11. Limit comments per page
While it’s awesome to get so much attention on your blog posts, a ton of comments can also slow page load time down. Breaking the comment section into pages is a good idea to shave off the time it takes for them to load.
To limit the number of comments that appear per page, simply go to Settings -> Discussion and check the “Break comments into pages” box. You can then select the number of comments per page (default is set to 50).
This should help improve memory consumption and boost page load times for posts and pages with tons of comments.
12. Reduce redirects
Redirects have some uses, but unnecessary redirects, such as 301 redirects and redirect chains, can really slow things down. It’s best to reduce the amount of additional information requests that your server undertakes.
13. Reduce post revisions
Post revisions save every content edit you make infinitely, which can make your site run slower. To speed up your site, you can choose to limit the number of revisions per post.
To do so, open the wp-config.php file and add this line of code to limit the number of post revisions:
define( ‘WP_POST_REVISIONS’, 4 );The number, in this case, denotes four, which means there will be four revisions created per post. You can change this number or even switch revisions off by setting the value to 0 or false.
14. Disable pingbacks and trackbacks
While you might have never heard of pingbacks or trackbacks before, some consider them a legacy feature. However, it’s still a good idea to make sure they are turned off, as they can slow down page speed.
To disable pingbacks and trackbacks, simply go to Settings -> Discussion and make sure “Allow link notifications from other blogs…” is unchecked.
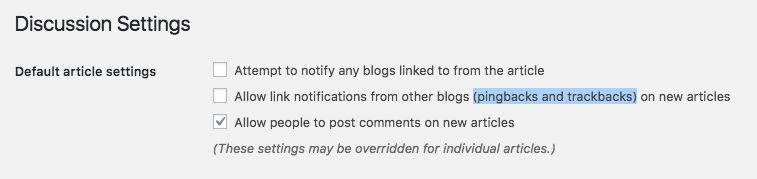
15. Run the latest version of PHP
Running the latest version of PHP can significantly affect your site’s speed. To determine if your site is ready to switch to the latest PHP environment, try using WP Engine’s PHP Compatibility Checker plugin.
Updating to the latest version of PHP on your own is also easy and can be done by going to your WP Engine user portal.
16. Choose a fast, lightweight theme
Not all themes are created equal—some are written better than others, and a beautiful UI design is meaningless if your site fails to load fast.
Rather than opting for a feature-rich theme (which involves a lot of code that has to be loaded every time someone visits your site), take a minimal approach by using a theme that contains the bare bones of what is necessary to function well.
Of course, you want the theme to look good. Make sure and check out WP Engine’s suite of premium WordPress themes, which are available to customers at no extra charge.
17. Use a CDN
No matter a user’s location, your content should be delivered blazing fast. Sometimes this isn’t always feasible, though—that is, if your site isn’t on an infrastructure that contains data centers in other parts of the world. Distance can mean lag in content delivery, which is where a content delivery network (CDN) becomes handy.
A CDN leads to faster page load times because when configured, your website will use an optimized server that’s closest to your site visitor. The data center will store static content and files, and then deliver them to users based on their location. This can help reduce external HTTP requests because the static content is already ready to go instead of requesting tons of HTTP at once.
Choosing a CDN depends on your site’s popularity and needs. Some WordPress CDN solutions include MaxCDN, Cloudflare, or CacheFly. WP Engine uses Cloudflare’s CDN for our customers.
18. Leverage browser caching
When your web server has HTTPS headers set up to specify cache expiration time, it also includes browser directives on how long the web page should be cached in your visitor’s browser. This tells your visitor’s browser to download the elements of your website (like CSS, JavaScript, and images) from their machine’s local disk rather than from the network. Since this means the browser has fewer network connections to make, this will help ensure your web page loads faster for them.
It’s also important to ensure your HTTPS headers include an expiration date so the browser knows when to get the resources from the network as if they were new, rather than getting them from their local machine.
At WP Engine, we take care of this piece for you since our servers are already optimized to serve WordPress websites. By default, pages are set to expire every ten minutes, and static resources are set to expire every 365 days.
19. Move to a dedicated server
If your site receives a lot of traffic, it’s a wise idea to host it on a dedicated server, where server resources are not shared.
When uptime is crucial, a shared server could be troublesome. Even though shared hosting is affordable, being on the same server as others can lead to clogging of CPU and RAM. It’s like being in an apartment complex and you only have so much water to share—if another site hogs up all the server’s bandwidth, then you are left with a slow running site/server and potential downtime.
To ensure your site has maximum uptime, it’s worth investing in a hosting plan where you receive the full resources of a single server.
21. Consider your hosting infrastructure
The hosting environment you choose can dramatically impact site speed in a positive way. Depending on the server and technology, managed hosting built for WordPress is necessary for a faster WordPress site.
Sites on WP Engine’s hosting environment have shown an average site speed improvement of 68%. Here are just a few of the ways WP Engine helps with site speed:
- EverCache: Our comprehensive multi-tier caching system, EverCache helps serve more cached pages to your end users. When cached, your pages are served in a few milliseconds, compared to a few full seconds when generating the page without cache. EverCache also caches the results of repeated queries to your database for faster performance. These layers combined mean faster performance and a more lightweight website that can support your site through waves of high traffic.
- Caching: We disallow caching plugins on our platform because we do it better. Our hosting platform provides caching for pages, objects, CDN management, URL rewriting, and more.
- Sophisticated infrastructure: All web traffic is handled by our sophisticated front-end system. This proprietary layer is built off of thousands of carefully designed code rules which are continually audited and adjusted for maximum performance and finely tuned for WordPress.
Want a third-party perspective on the pros and cons of using WP Engine? Check out this WP Engine review.
21. Speed up your site with a WordPress plugin
WordPress has a huge plugin ecosystem that can make performance optimizations easier. Here are a few plugins focused specifically on speeding things up.
- Perfmatters: This plugin allows you to disable WordPress default options that you’re not using.
- WP Super Minify: This tool allows you to combine and compress files for quicker loading.
- Smush: This plugin optimizes your images so they don’t slow down your page.
While each of these plugins offers a straightforward way to optimize particular aspects of your WordPress site, it’s important to note that they’re focused on individual, specific areas and will optimize only those parts of your site.
Using caching plugins to accelerate WordPress
Caching is fundamental to WordPress speed optimization. It involves storing static HTML versions of your pages, so they don’t need to be dynamically generated by PHP and the database for every visitor. This dramatically reduces server load and speeds up delivery. Object caching, similarly, stores results of common database queries.
Popular caching plugins like WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache, and WP Super Cache can manage this process. General setup involves installing the plugin, enabling page caching, and configuring options like cache preloading (generating cached files proactively). However, a crucial pitfall is “double caching.”
Many managed hosts for WordPress, including WP Engine with its proprietary EverCache system, provide robust server-level caching. Installing a separate caching plugin in such environments is often unnecessary and can lead to conflicts or unexpected behavior. Always check your hosting provider’s documentation first; you might already have optimal caching configured.
To validate if caching is working (either server-level or plugin-based), you can use browser developer tools to inspect the HTTP response headers (look for `cache-control` headers or specific headers added by the caching system/plugin) or check the page’s source code for comments indicating a cached version is being served. Implementing caching correctly is a key step to speed up WordPress site performance.
Enable GZIP and Brotli compression for smaller payloads
To further increase WordPress speed, especially for users on slower connections, enabling server-level compression is vital. Technologies like GZIP and the more modern Brotli compress text-based files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) before they are sent from your server to the visitor’s browser.
The browser then decompresses these files, resulting in significantly smaller download sizes—often reducing file sizes by 70% or more. This reduction in data transfer leads to faster loading times, lower bandwidth consumption, and can improve your site’s Time to First Byte (TTFB).
Most quality hosting providers, including WP Engine, enable GZIP or Brotli compression automatically at the server level, as this is the most efficient method. If your host doesn’t, or you manage your own server, compression can typically be enabled by adding specific directives to your server configuration files (like `.htaccess` for Apache servers or `nginx.conf` for Nginx servers).
While some optimization plugins offer options to enable GZIP, server-level configuration is generally preferred. You can verify if compression is active using online checker tools or by examining the `content-encoding` response header in your browser’s developer tools. Ensuring compression is active is a standard best practice for improving WordPress speed.
Keep WordPress core, themes, and plugins updated
Keeping your WordPress ecosystem up-to-date is paramount not only for security but also for optimal WordPress performance. Updates for WordPress core, themes, and plugins frequently include performance enhancements, bug fixes, and compatibility improvements that can directly make WordPress faster. Outdated software might contain inefficient code or known bottlenecks that developers have since resolved. Best practices for updates include: Always test updates on a staging environment first.
This is critical to catch any potential conflicts or issues before they affect your live site; hosts like WP Engine provide easy one-click staging environments. Consider enabling automatic updates for minor core releases (which usually focus on security and maintenance), but exercise caution with major core, theme, or plugin updates, preferring manual testing on staging.
For developers managing multiple sites, using WP-CLI (`wp core update`, `wp plugin update –all`, etc.) offers an efficient way to handle updates. After applying any updates to your live site, thoroughly check its functionality and monitor its speed to ensure everything is working correctly. Regular updates are a cornerstone of maintaining a secure and high-performing website.
Optimize your WordPress homepage for faster first impressions
- Limit the Number of Posts Displayed: If your homepage shows your latest blog posts, configure it (Settings > Reading) to display a smaller number (e.g., 5-7) rather than the default 10 or more. Fewer posts mean less data to load initially.
- Show Excerpts, Not Full Posts: Complementing the point above, ensure you’re displaying post summaries (excerpts) instead of the full content on your homepage and archive pages. This dramatically reduces page size and load time, contributing significantly to WordPress website speed optimization. Check Settings > Reading or your theme’s customization options.
- Rethink Heavy Sliders and Carousels: Large, JavaScript-heavy image sliders above the fold can severely impact LCP. Consider using a static, optimized hero image or a highly optimized, lightweight slider if absolutely necessary.
- Minimize and Defer Widgets: Remove any unnecessary widgets from your homepage’s sidebar or footer. Widgets loading external scripts (like social feeds or complex ads) should be deferred if possible or replaced with lighter alternatives to improve WordPress website speed.
- Optimize Above-the-Fold Content: Focus on loading only the essential CSS and JavaScript needed to render the initial viewport quickly. Techniques like inlining critical CSS and deferring non-essential scripts can make a noticeable difference in perceived load time.
Enhance WordPress search with Elasticsearch
For websites with substantial content, the default WordPress search functionality can become slow and resource-intensive, as it relies on direct MySQL database queries that don’t always scale well. This can negatively impact user experience and overall WordPress performance. Elasticsearch provides a powerful alternative – it’s a dedicated, open-source search and analytics engine built for speed and relevance.
By offloading search queries from your WordPress database to an Elasticsearch cluster, you can drastically reduce server load and deliver significantly faster, more accurate search results to your users. Implementing this typically requires access to an Elasticsearch server or service and using a WordPress plugin like ElasticPress to index your site’s content and handle the communication between WordPress and Elasticsearch.
Some hosting providers, including WP Engine on specific plans, offer integrated Elasticsearch solutions, simplifying the setup and maintenance required to leverage this technology and effectively speed up WordPress site search capabilities.
Combine external CSS and JavaScript files in WordPress
A common strategy to improve WordPress website speed involves reducing the number of HTTP requests the browser needs to make. WordPress sites often load numerous individual CSS stylesheets and JavaScript files from the theme, plugins, and core itself.
Combining these multiple files into fewer, larger files (a process called concatenation) can decrease loading overhead. Optimization plugins like Autoptimize or Asset CleanUp often include features to automatically combine CSS and JavaScript files (alongside minification).
However, it’s crucial to approach this with caution. Combining files can sometimes break your site if scripts rely on a specific loading order (dependencies). Thorough testing on a staging site is absolutely essential after enabling file combination.
It’s also worth noting that with modern web protocols like HTTP/2 and HTTP/3, which allow parallel requests over a single connection, the benefits of concatenation are less significant than they once were, though it can still provide gains in some scenarios. Always test and measure the impact of this technique as part of your WordPress speed optimization efforts.
Streamline comments: paginate or disable to boost speed
While comments foster engagement, a large number of them on a single post can significantly slow down page loading times. Each comment adds to the database query load and increases the amount of HTML the server must generate and the browser must render, impacting your WordPress speed.
To mitigate this, WordPress offers a built-in solution: comment pagination. Navigate to Settings > Discussion and check the box for “Break comments into pages,” setting a reasonable number (e.g., 25-50) of top-level comments per page. This prevents loading hundreds or thousands of comments at once.
Additionally, consider using plugins that lazy-load the comments section or Gravatar images, so they only load when the user scrolls near them. For sites where comments aren’t crucial or become unmanageable, disabling them entirely (either globally in Discussion settings or on specific posts/pages) is the most direct way to eliminate their performance impact and potentially make WordPress faster.
WordPress performance optimization best practices
- Conduct Regular Performance Audits: Don’t treat optimization as a one-time task. Periodically test your key pages using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, WebPageTest, or GTmetrix to monitor your WordPress speed and catch regressions introduced by new content, plugins, or updates.
- Utilize Staging Environments Diligently: Before applying any significant changes (plugin updates, theme switches, custom code, optimization settings) to your live site, always test them thoroughly on a staging copy. This prevents unexpected errors or performance degradation on your production site. Platforms like WP Engine make staging easy.
- Implement Proactive Monitoring: Use application performance monitoring (APM) tools like New Relic (often available through hosts like WP Engine) or WordPress plugins like Query Monitor to identify slow database queries, PHP errors, external API call delays, and other backend bottlenecks affecting WordPress performance in real-time.
- Leverage Automation and Efficiency Tools: Use WP-CLI for command-line management of updates, database tasks, and other repetitive actions. Implement automated image optimization workflows upon upload. Efficiency saves time and reduces manual errors.
- Establish and Adhere to a Performance Budget: Define clear, measurable goals for key performance metrics (e.g., LCP under 2.5 seconds, total page size under 1.5MB, fewer than 60 requests). Evaluate new features, plugins, or design changes against this budget to ensure they don’t compromise your efforts to speed up WordPress site performance.
- Prioritize Mobile Optimization: Given that mobile traffic often exceeds desktop traffic, consistently test and optimize for various mobile devices and network conditions. Mobile performance is critical for user experience and SEO rankings.
- Perform Regular Cleanups: Periodically audit and remove unused themes, plugins, and media files. Clean up your database by removing old post revisions, transients, and spam comments using plugins like WP-Optimize or Advanced Database Cleaner. Reducing bloat is key to ongoing WordPress speed optimization.
FAQs
Why is website speed important for my WordPress site?
Site speed has a significant impact on businesses, as slow load times can lead to unhappy users, high bounce rates, and ultimately lost sales. In addition to influencing user experience, slow website speed can also hurt your SEO rankings.
How fast should my WordPress site load?
Google recommends a load time of three seconds or less for your website to meet best practices. Webpages that take five seconds or more to load have an increased probability of a bounce.
What are common causes of slow loading times on WordPress sites?
There are many factors that can influence load times for WordPress sites, but some of the most common causes of slow site speed include heavy or poorly coded plugins, large or unoptimized image files, excessive HTTP requests, ineffective caching, bloated themes, and slow web hosting.
How often should I test and optimize my WordPress site speed?
It’s important to test your site’s speed regularly to maintain optimal site speed performance. We recommend testing site speed monthly or following any major site changes (like adding a new plugin or making major content changes).
Is managed WordPress hosting worth it for improving site speed?
Managed WordPress hosting can significantly improve site speed for your WordPress site. With a managed host, your website will benefit from reliable infrastructure built just for WordPress sites, a tech stack tailored for WordPress, and access to an expert support team.
Boost your WordPress performance: Speed up WordPress with WP Engine
All of the steps contained in this guide can help you improve the speed of your WordPress site as well as the user experience you provide to site visitors.
If you’re looking for the most effective way to speed up your WordPress site(s), WP Engine’s powerful platform and extensive set of developer tools are the way to go. Find out how our industry-leading hosting for WordPress and solutions like Page Speed Boost can help you speed up your website today!
